back to the OSM tools main page
spatialite_osm_raw
Syntax:
usage: spatialite_osm_raw ARGLIST
==============================================================
-h or --help print this help message
-o or --osm-path pathname the OSM-file path
both OSM-XML (*.osm) and OSM-ProtoBuf
(*.osm.pbf) are indifferenctly supported.
-d or --db-path pathname the SpatiaLite DB path
you can specify the following options as well
-cs or --cache-size num DB cache size (how many pages)
-m or --in-memory using IN-MEMORY database
-jo or --journal-off unsafe (but faster) mode
|
Example:
$ spatialite_osm_raw -o my_country.osm.pbf -d my_country.sqlite
SQLite version: 3.7.11
SpatiaLite version: 3.1.0
inserted 3047972 nodes
166634 tags
inserted 233481 ways
423462 tags
3461321 node-refs
inserted 6068 relations
14815 tags
56617 refs
$
|
the above shown command must be invoked from the shell:
- -o my_country.osm.pbf selects the OSM input file (in this case, of the OSM-protobuf format).
- -d my_country.sqlite selects the SpatiaLite's DB-file to be created and populated.
- you can eventually add any other DB-related optimization switch, if you think it will be useful.
Want to learn more ? read the DB optimization short note
Once the command succesfully completes its execution, you'll find a brand new DB-file just created ...
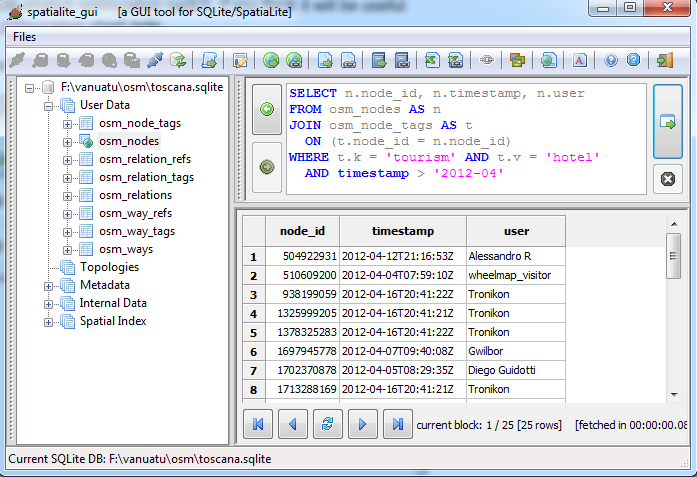
... you can explore this DB-file e.g. using spatialite_gui and executing any SQL query at your will.
e.g. in this case we are extracting all Nodes exposing the tourism:hotel tag, and being inserted since April 2012.
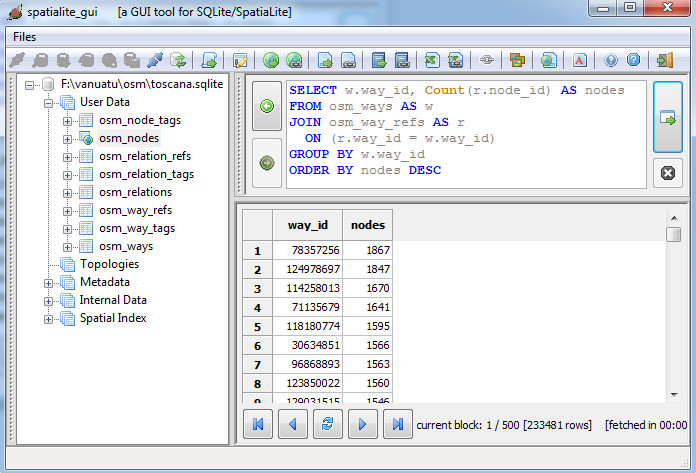
this further query will extract all Ways, determining their complexity (i.e. the number of referenced Nodes).
the resultset will be ordered so to show the most complex Ways first.
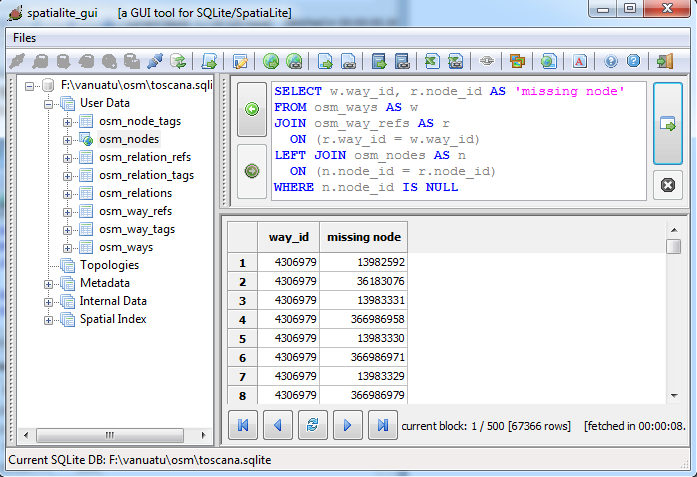
this last example query will extract all Ways, checking for broken Node references.
i.e. it will check if some undefined Node is referenced anyway, thus identifying the corresponding invalid Way.
back to the OSM tools main page